Development and Evaluation of Parkinson's Disease-Dyad Multidisciplinary Illness Management Program (PD-DMMP)
based on Longitudinal Investigation(2022~2027)
Funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant, Korea government (MSIT) (2022R1A2C1011038)
In 2021, the Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency announced plans to establish a national cohort for Parkinson's disease, but it lacked information on caregivers, non-motor symptoms, and key psychosocial factors critical to patient management and health outcomes. The relationship between Parkinson's patients and their caregivers is not independent; effective disease management behaviors are achievable when patient-caregiver evaluations align. Sequential evaluations and management behaviors can contribute to not only the individual health of patients and caregivers but also to dyadic health.
We are conducting a three-year data collection study with Parkinson’s patients and caregivers aged 50 and older, in stages 2–4 on the Hoehn & Yahr scale, across two university hospitals. Based on analyses of prospective longitudinal data and a systematic review, this research aims to develop the PD-DMMP. Ultimately, the PD-DMMP seeks to improve the health and quality of life of both Parkinson’s patients and their caregivers.
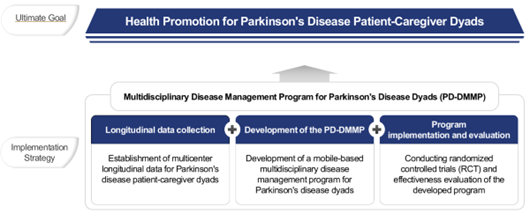
[Research strategy & final goal]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Oodlm6_F5C8
The Effect of VR-REST on Nurses' Patient Safety Knowledge and Learning Self-Efficacy: Focusing on Nurses at General Hospitals in the Busan, Ulsan, and Gyeongnam(2022~2025)
Funded by the Ministry of Education through the 4th BK21 Graduate School Innovation Support Project, supported by Yonsei 'Eokkaedongmu Project'
Despite government efforts, patient safety remains a major public health issue in Busan, Ulsan, and Gyeongnam, with a steady incident rateIn South Korea, healthcare resources are heavily concentrated in the Seoul metropolitan area, underscoring the need to improve the healthcare system's regional balance. In 2023, reports from healthcare institutions indicated that patient safety incidents were relatively high not only in the metropolitan area (Seoul 25.5%, Gyeonggi 21.9%), but also in regions such as Busan (8.1%) and Gyeongnam (8.1%). There is a need to strengthen patient safety competencies, especially among nurses in general hospitals within the Busan-Ulsan-Gyeongnam region.
The "Virtual Reality-Room of Errors Simulation Training(VR-REST)" virtual simulation training program provides nurses with a safe environment to practice identifying patient safety threats through critical thinking and situational awareness. To enhance immersion, we filmed clinical settings using 360-degree cameras, creating a highly engaging experience. Accessible on a web platform and compatible with VR headsets, this program aims to enhance patient safety by allowing nurses to study realistic clinical scenarios and potential errors in depth.

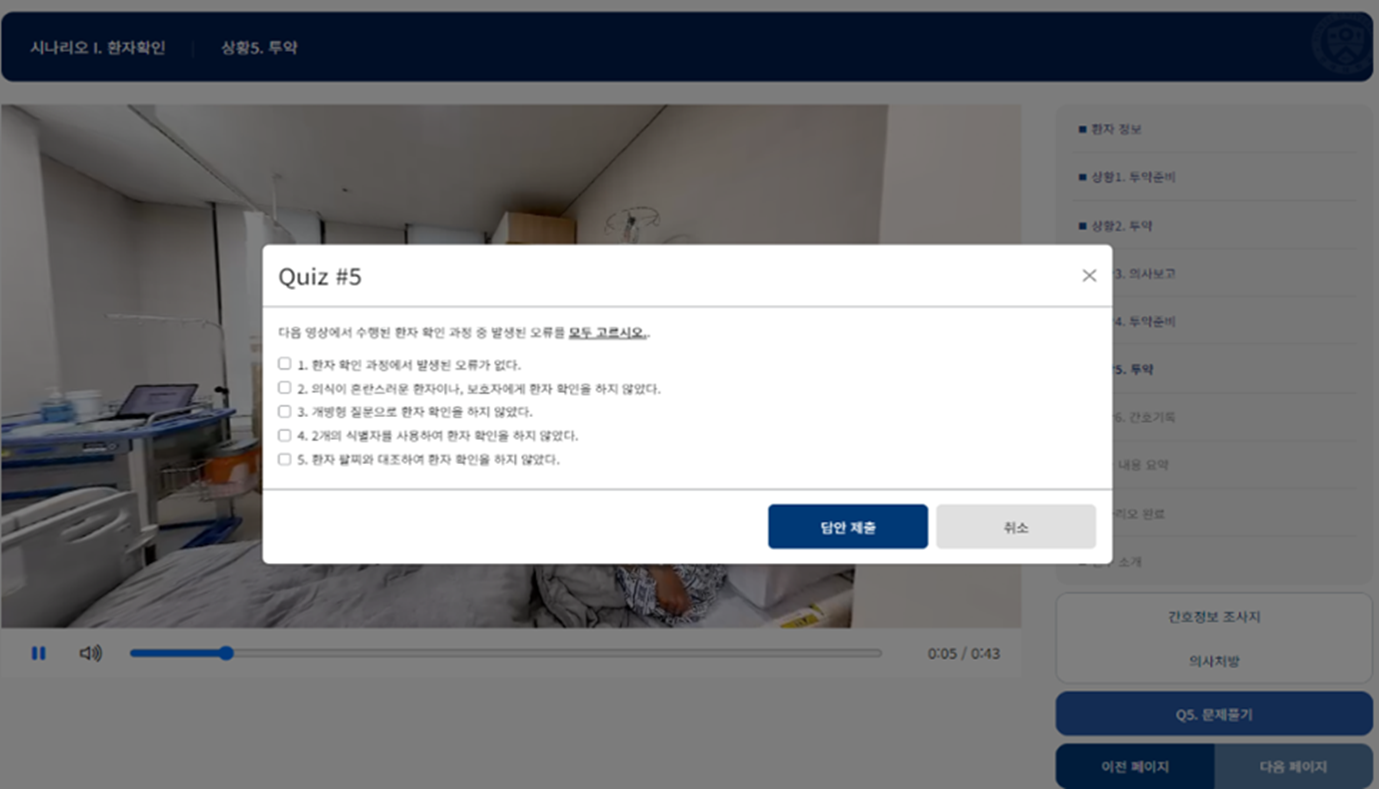
[Scene of room of errors virtual simulation program]
https://buly.kr/1GIsCv6
The Impact of a Non-Motor Symptom Management Application
on the Quality of Life in Parkinson's Disease Patients(2018~2022)
Funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant, Korea government (MSIT) (2018R1D1A1A0208555913)
Many Parkinson's disease patients may not associate non-motor symptoms such as constipation, depression, fatigue, sleep disturbances, dysphagia, and autonomic dysfunction with the disease itself. However, non-motor symptoms often negatively impact quality of life more than motor symptoms. Self-management, where patients monitor their symptoms, recognize changes, and engage in health-promoting behaviors, is essential. Most applications to support self-management for Parkinson’s patients focus only on motor symptoms, lack a comprehensive system for tracking personal health management, and do not allow interaction with healthcare professionals, limiting their effectiveness.
We assessed the needs for symptom management in Parkinson's disease patients and, through technical collaboration with Magelwon Co., developed a Non-Motor Symptom Management Application. To evaluate the effectiveness of the application, a randomized controlled pre-post repeated measures experimental study was conducted with Parkinson’s disease patients aged 60 and older at a university hospital. The results showed that monitoring non-motor symptoms through the application improved self-management, thereby enhancing the quality of life for Parkinson’s patients.

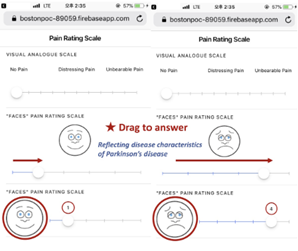
[Storyboard of non-motor symptom management application]
https://journals.lww.com/cinjournal/fulltext/2024/04000/a_mobile_app_for_comprehensive_symptom_management.7.aspx
Analysis of an impact of nurse navigator in patients
with Parkinson's disease(2015~2018)
Funded by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant, Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning
(NRF-2015R1A1A3A04001474)
The development of a navigator for Parkinson's disease patients and their primary caregivers analyzed how medical service needs and satisfaction impact self-efficacy, quality of life, and caregiving appraisal. Through this process, the validity of the navigator was verified using the Delphi technique with a panel of experts, and a pilot study was conducted. Ultimately, the effectiveness of the navigator was confirmed through a randomized controlled trial.
Effects of Group Exercise Program in Parkinson's Disease(2012~2015)
Funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant (NRF-2012R1A1A3012645)
Patients with Parkinson’s disease face increasing challenges in daily activities and independence loss due to motor symptoms like tremors, bradykinesia, and gait disturbances, significantly impacting their quality of life. Parkinson's disease is a chronic condition that can be managed through the patient's efforts to implement medical services and treatment instructions. Therefore, it is important to provide nursing interventions aimed at reducing clinical symptoms and improving the quality of life for Parkinson's patients. Exercise, emphasizing strength, endurance, and balance, is particularly beneficial, enhancing mobility, supporting daily activities, and reducing fall risks, making it a crucial component of care for Parkinson’s patients.
We developed an exercise program for Parkinson's disease patients based on previous research focused on exercise programs and function-focused care. The program’s content was validated, and a pilot study was conducted. To assess its effectiveness, we recruited 40 Parkinson's disease patients aged 50 and older and conducted a randomized controlled trial. The results demonstrated that this nursing intervention program promoted physical abilities, improved activities of daily living and physical fitness, enhanced physical independence, and improved health-related quality of life. These findings provide evidence supporting the development of intervention programs for Parkinson's disease patients.

[The content of the group exercise program in Parkinson's disease]
https://buly.kr/Cho7y2o
https://buly.kr/5q6ZiEk